In printing and paper production, “A4” is one of the most commonly used paper sizes worldwide. From office documents and brochures to manuals and packaging inserts, A4 plays a vital role in daily printing applications. Understanding what A4 means, why it’s used, and how it’s produced helps businesses choose the right paper and equipment for efficient, standardized printing.
A4 is a standard paper size defined by the ISO 216 international paper standard. It measures 210 × 297 millimeters (8.27 × 11.69 inches). The A-series is based on a simple and logical system: when a sheet is folded in half parallel to its shorter side, it becomes the next size down (A4 folded becomes A5, A3 folded becomes A4). Because of this consistency, A4 has become the default paper size for documents in most countries around the world.
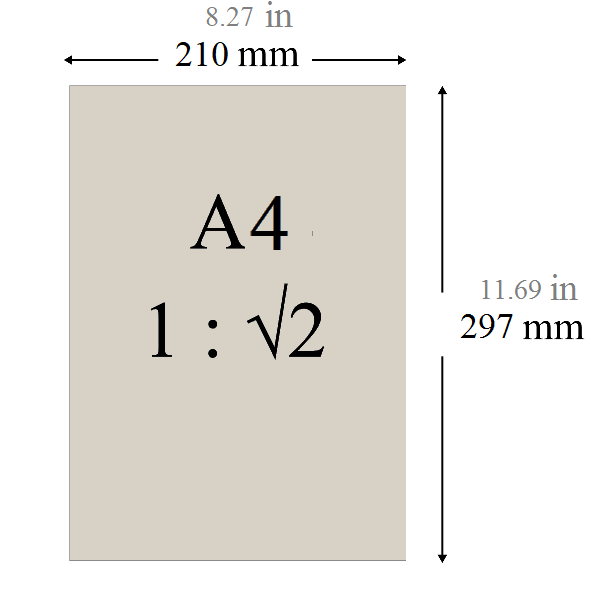
Standardized dimensions: 210 × 297 mm
Aspect ratio: √2 : 1, allowing easy scaling without distortion
Global compatibility: Accepted across Europe, Asia, and many other regions
Versatile usage: Suitable for text, graphics, and mixed-content printing
These characteristics make A4 ideal for both digital printing and traditional offset printing.
A4 paper is widely used because it balances practicality, efficiency, and compatibility:
Universal acceptance: Most printers, copiers, and scanners are designed around A4
Cost efficiency: Optimized for mass production and minimal waste
Professional appearance: Ideal size for letters, reports, contracts, and manuals
Easy storage and handling: Fits standard folders, binders, and envelopes
For businesses engaged in international trade or large-scale printing, A4 ensures smooth communication and consistent presentation.

The production of A4 paper involves a series of standardized processes, from raw material preparation to final cutting and packaging. Below is a detailed overview of the production workflow, with a focus on Hongke's A3/A4 Producing Line.
1. Raw Material Preparation: The main raw materials for A4 paper are wood pulp (softwood or hardwood) and recycled paper. Wood pulp is processed to remove impurities, while recycled paper is sorted, cleaned, and pulped to form usable fiber materials.
2. Pulping: The raw materials are mixed with water and chemicals to break down into pulp, which is then refined to improve fiber quality. This step ensures the paper has the required strength and smoothness.
3. Paper Formation: The pulp is diluted and poured onto a wire mesh conveyor belt (Fourdrinier machine) to form a continuous paper web. Water is drained from the pulp through gravity and suction, solidifying the fibers into a wet paper sheet.
4. Pressing and Drying: The wet paper sheet is passed through a series of press rolls to remove excess water, then dried using heated cylinders to reduce moisture content to the standard level (approximately 5-8%).
5. Calendering: The dried paper is run through calender rolls to smooth the surface, improve thickness uniformity, and enhance printability.
6. Reeling and Cutting: The continuous paper web is reeled into large rolls. These rolls are then cut into A4-sized sheets using precision cutting machines. The cutting process strictly adheres to ISO 216 size and tolerance requirements.
7. Quality Inspection and Packaging: The cut A4 sheets are inspected for size accuracy, thickness, smoothness, and defects. Qualified products are counted, stacked, and packaged for distribution.
Modern production relies on automated paper converting lines to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Hongke’s A3/A4 Producing Line is designed specifically for this purpose. It integrates high-speed cutting, precise stacking, and automatic counting, enabling manufacturers to produce both A3 and A4 sheets with minimal waste and stable quality. With advanced control systems and reliable performance, Hongke’s A3/A4 Producing Line helps paper mills and converters meet high-volume market demand while maintaining international standards.
Although A4 is the global standard, the United States primarily uses U.S. Letter size.
| Feature | A4 | U.S. Letter |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | 210 × 297 mm | 8.5 × 11 inches |
| Aspect ratio | √2 : 1 | Not standardized |
| Global use | International standard | Mainly U.S. & Canada |
| Scaling efficiency | Excellent | Less efficient |
This difference is important for international printing projects, as layouts may shift if the wrong paper size is used.
A4 in printing refers to a globally standardized paper size that ensures consistency, efficiency, and compatibility across industries. Its balanced dimensions, wide acceptance, and ease of production make it the preferred choice for documents worldwide. With advanced solutions like Hongke’s A3/A4 Producing Line, manufacturers can efficiently produce high-quality A4 paper to meet modern printing demands.
Q1: Is A4 the same as Letter size?
No. A4 is slightly narrower and taller than U.S. Letter and follows a different standard.
Q2: Why is A4 used more internationally than Letter size?
Because A4 is part of the ISO 216 system, which is recognized and adopted by most countries.
Q3: Can printers handle both A4 and Letter size?
Many modern printers support both, but correct settings are required to avoid scaling issues.
Q4: Can the same production line make A3 and A4 paper?
Yes. Equipment such as Hongke’s A3/A4 Producing Line is designed to flexibly produce both sizes with high precision.
Q5: What industries most commonly use A4 paper?
Office printing, education, publishing, packaging inserts, and commercial printing all rely heavily on A4 paper.

GET A QUOTE